Linear Approximation Calculator
Calculate linear approximations step by step
The calculator will find the linear approximation to the explicit, polar, parametric, and implicit curve at the given point, with steps shown.
Related calculator: Quadratic Approximation Calculator
The Linear Approximation Calculator uses a linear function to approximate the value of a more complex function. It allows you to calculate linear approximations of explicit, parametric, polar, or implicit curves at a given point.
How to Use the Linear Approximation Calculator?
Input
Begin by choosing the type of function you have, whether it's explicit, parametric, polar, or implicit. Input the function you want to approximate. Input the point at which you wish to obtain the linear approximation.
Calculation
After you have filled in all the fields, click the "Calculate" button.
Result
The calculator will provide the linear approximation of the function at the specified point.
What Is Linear Approximation?
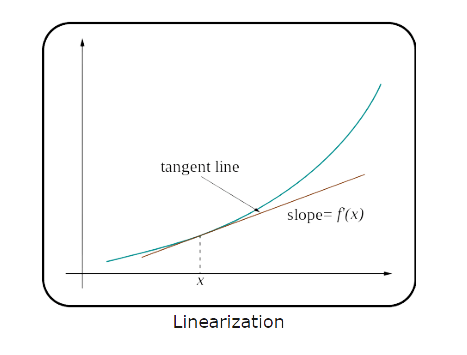
Linear approximation, sometimes called the tangent line method, is a fundamental technique in calculus. It uses the tangent line of a function at a specific point to estimate the function's value near that point.
To put it plainly, consider some function and the curve it represents. Let's pick a point on that curve and draw a straight line (tangent line) that touches the curve at that point. This line can estimate the function values near the chosen point. This approach got its name "linear approximation" due to the linear nature of the tangent used for the estimate.
The formula for linear approximation is
L(x)=f(a)+f′(a)(x−a),where:
- L(x) is the linear approximation of the function f(x) at x=a.
- f(a) is the actual value of the function at the point x=a.
- f′(a) denotes the derivative (or slope) of the function f(x) at the point x=a.
The idea of linear approximation is that, over short intervals, the behavior of a function can be approximated by the behavior of its tangent line. This becomes especially useful in situations where exact calculations of the value of a function can be very difficult and impractical. For example, it can be used in engineering, physics, or other scientific fields to simplify complex tasks.
How to Do Linear Approximation?
Consider the function f(x)=√x. Suppose we're interested in approximating the value of this function at x=4.01, using the known value at x=4.
Find the Derivative
The derivative of f(x) is
f′(x)=12√xEvaluate the Derivative at x=4
f′(4)=12√4=14Use the Linear Approximation Formula
Plug the values into the formula to estimate f(4.01):
L(4.01)=f(4)+f′(4)(4.01−4)L(4.01)=2+14⋅0.01L(4.01)=2+0.0025=2.0025
Thus, using linear approximation, √4.01 is approximately 2.0025.
Although this is a simple example, it emphasizes the power of linear approximation. It provides a quick estimate, which is especially useful in situations where an exact value is not needed or its calculation is too complicated or too slow.
Why Choose Our Linear Approximation Calculator?
Precision
Our calculator goes through rigorous testing to ensure it always delivers accurate results.
User-Friendly Interface
We've designed our calculator with users in mind. Its intuitive layout ensures that even those unfamiliar with linear approximation can easily use it.
Functionality
In addition to basic explicit functions, our calculator can handle a wide range of functions, including parametric, polar, and implicit curves.
Speed
Our calculator gives instant results, eliminating complicated manual calculations.
FAQ
What is linear approximation?
Linear approximation is a calculus method used to estimate the value of a function near a specific point by using the slope of the tangent line to the function at that point. It replaces complex curves with straight-line approximations for easier calculations.
How does the Linear Approximation Calculator work?
Our calculator uses the tangent line approximation formula to estimate a function's value near a given point. It takes the function and the point and calculates the linear approximation using the derivative, whose value at that point is the slope of the tangent line at that point.
What types of functions can I use with the calculator?
Our calculator is versatile and can handle various functions, including explicit, parametric, polar, and implicit curves.
